Thursday, 29 September 2011
Tuesday, 20 September 2011
Pro-Desktop (Converting Diagram Into DXF File)
1. Create design and save (Do Not Close Window)
2. Create new engineering drawing (File / Engineering Drawing)
3. Choose template (note - for this tutorial I chose bottom right picture)
3. Remove the box in the bottom right corner by going to Sheet 1 / Sheet Setup (If you chose bottom right picture)
4. This box should appear (select Specify Format and choose ISO - A2)
5. The box has been removed
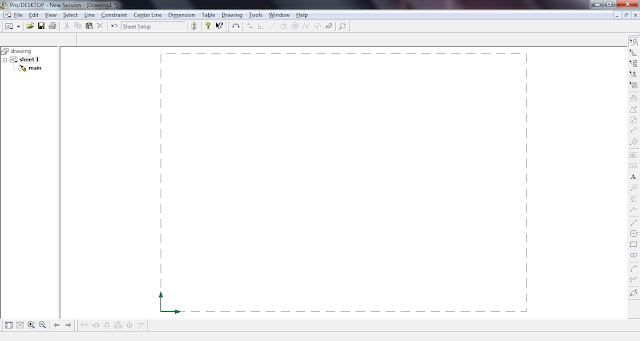
6. Input your design by going to Drawing / Add Modelling View
7. Select you design and press OK (Note - the chosen design must be open in a different window)
8. Move your design to save material by click and dragging it
9. Save your drawing
10. Export it as a DXF file by choosing File / Export / DXF File
11. Choose where you want to save the dxf file and select correct properties and press OK
2. Create new engineering drawing (File / Engineering Drawing)
3. Choose template (note - for this tutorial I chose bottom right picture)
3. Remove the box in the bottom right corner by going to Sheet 1 / Sheet Setup (If you chose bottom right picture)
4. This box should appear (select Specify Format and choose ISO - A2)
5. The box has been removed

6. Input your design by going to Drawing / Add Modelling View
7. Select you design and press OK (Note - the chosen design must be open in a different window)
8. Move your design to save material by click and dragging it
9. Save your drawing
10. Export it as a DXF file by choosing File / Export / DXF File
11. Choose where you want to save the dxf file and select correct properties and press OK
Monday, 12 September 2011
Compression Moulding
What is Compression Moulding?
Compression Moulding is a process where molten plastic is compressed to create a shape. The molten plastic then takes the shape of the mould. This is the only process capable of of moulding thermosetting plastics.
Compression Moulding is a process where molten plastic is compressed to create a shape. The molten plastic then takes the shape of the mould. This is the only process capable of of moulding thermosetting plastics.
Injection Moulding
What is Injection Moulding?
Injection Moulding is a process of moulding where the material is injected into the mould to create a product. The material (usually granulated or powdered thermoplastics) is heated so that it becomes a liquid state and then forced under pressure into a mould. The material into the mould cools forming a part / product.
Injection Moulding is a process of moulding where the material is injected into the mould to create a product. The material (usually granulated or powdered thermoplastics) is heated so that it becomes a liquid state and then forced under pressure into a mould. The material into the mould cools forming a part / product.
click for animation
Rotational Moulding
What is Rotational Moulding?
Rotational moulding is a process in which hollow parts/products are manufactured. The most common material used is plastic to create products such as plastic balls. The material is heated up so that it becomes a liquid state. It is then rotated, once the liquid has taken the shape of the mould water or air is used to cool the material. The material then becomes a solid state. The mould is then broken apart to reveal the product.
Rotational moulding is a process in which hollow parts/products are manufactured. The most common material used is plastic to create products such as plastic balls. The material is heated up so that it becomes a liquid state. It is then rotated, once the liquid has taken the shape of the mould water or air is used to cool the material. The material then becomes a solid state. The mould is then broken apart to reveal the product.
Thursday, 8 September 2011
Polymers (Thermoplastic Products Characteristics)
WORK IN PROGRESS - WILL BE FINISHED BY END OF WEEK
Polymers (Thermosetting Products Characteristics)
WORK IN PROGRESS - WILL BE FINISHED BY END OF WEEK
Polymers (Thermosetting Plastics)
Here are the types of Thermosetting Plastics:
- Epoxy Resins
- Melamine Formaldehyde
- Polyester Resins
- Urea Formaldehyde
Polymers (General Characteristics of Plastics)
Here are some general characteristics of plastics:
- Good electrical and thermal insulators
- Good strength to weight ratio
- Good resistance to atmospheric and chemical erosion
- Low melting point
- Lightweight
- Wide range of colours (due to pigments) and transparency
- Main categories are Thermosetting and Thermoplastic
Products Made From Polymers
Here are some examples of some products made from Polymers:
Hardhat - ABS
Bucket - HDPE
Tubaware Boxes - PP
Outside Garden Lights - PMMA
Polystyrene Cup - PS
Gear Mechanism - NYLON
Wiring - PVC
Lab Glasses - PC
Washing Liquid Bottle - LDPE
Plastic Windows- uPVC
Plastic Coating For Cutlery - CA
Polymers (Thermoplastics)
Here are some Thermoplastics:
ABS - Acrylonitrile Butadiene Stryrene
CA - Cellulose Acetate
NYLON - Polyamide
PMMA - PolyMethylMethAcrylate (Acrylic)
PP - Polypropylene
HIPS - High Impact Polystrene
PS - Polystyrene
LDPE - Low Density Polyehthlene
HDPE - High Density Polyethlene
uPVC - Polyvynil Chloride
PVC - (Unplasticised Flexible) Polyvynil Chloride
PET - Poly Ethylene Terephtalate
PC - Polycarbonate
ABS - Acrylonitrile Butadiene Stryrene
CA - Cellulose Acetate
NYLON - Polyamide
PMMA - PolyMethylMethAcrylate (Acrylic)
PP - Polypropylene
HIPS - High Impact Polystrene
PS - Polystyrene
LDPE - Low Density Polyehthlene
HDPE - High Density Polyethlene
uPVC - Polyvynil Chloride
PVC - (Unplasticised Flexible) Polyvynil Chloride
PET - Poly Ethylene Terephtalate
PC - Polycarbonate
Thermosetting and Thermoplastics
There are two main types of polymers (Plastics) - Thermosetting and Thermoplastic.
Thermoplastic:
Thermoplastic:
- Thermoplastics soften when heated, once heated they can be moulded into any shape. After cooling down they harden. The main benieft of thermoplastics is that once moulded they can be reshaped.
Thermosetting:
- Thermosetting plastics soften when heated, once heated they can be moulded into any shape. After cooling down they harden. The main disadvantage is that once moulded they can't be reshaped.
Tuesday, 6 September 2011
Assignment One - I Should Never Of Purchased
A while back from now I purchased a brand new 32inch LED Samsung TV, at a cost of over £100, which was extremely thin and had a clear edges round the sides. Its function wasn't designed fully as within three days the TV decided to break whilst it was turned on. One moment it was working the next it was broken. Although the light that projects a green light when turned on was still on the actual screen was black.
The form of the TV was rectangle and was probably made from ABS as it needs to be durable, have a good strength to weight ratio and it must be non-toxic. The plastic had a shiny black finish.
Before it broke the function was great with built in freeview, an easy to read and understand guide and fantastic quality TV. The freeview was a brilliant extra as a few months before my area changed from Analogue to Digital so it meant we didn't have to buy a digital box
The fact that it was LED meant that Samsung were able to design it to be thinner that old style TVs.
A possible cause of the fault might be due to heavy usage of a TV by a family of 5 including 1 child and 2 teenagers. However the TV showed no fault in the first two days of use.
Despite the fact it had broken within three days of purchase I decided to claim it on the guarantee and I quickly received a new TV which still works today.
The form of the TV was rectangle and was probably made from ABS as it needs to be durable, have a good strength to weight ratio and it must be non-toxic. The plastic had a shiny black finish.
Before it broke the function was great with built in freeview, an easy to read and understand guide and fantastic quality TV. The freeview was a brilliant extra as a few months before my area changed from Analogue to Digital so it meant we didn't have to buy a digital box
The fact that it was LED meant that Samsung were able to design it to be thinner that old style TVs.
A possible cause of the fault might be due to heavy usage of a TV by a family of 5 including 1 child and 2 teenagers. However the TV showed no fault in the first two days of use.
Despite the fact it had broken within three days of purchase I decided to claim it on the guarantee and I quickly received a new TV which still works today.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)


































